LLNL's National Ignition Facility is the hottest place on earth for the briefest of moments during an experiment, as explained in a new paper in Physics of Plasmas.
Science and Technology Highlights
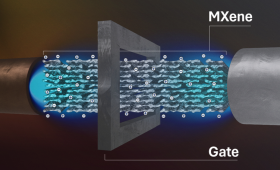
By applying voltage to electrically control a new “transistor” membrane, LLNL researchers achieved real-time tuning of ion separations.
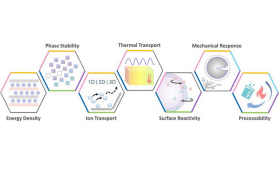
LLNL researchers outline how state-of-the-art computational modeling can help to unravel the fundamental relationships among battery processing, structure, properties.
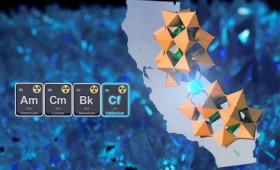
LLNL chemists are using a novel nanoscale synthesis and crystallization approach to create, isolate and structurally characterize a pure californium-containing compound.

In November, the Department of Energy Office of Science renewed the Superconducting Quantum Materials and Systems Center.

LLNL researchers and collaborators lay the foundation for understanding how POMs interact with some of the most chemically challenging actinide elements.

LLNL researchers aim to use a machine-learning model that can distinguish opioids from other chemicals with an accuracy over 95% in a laboratory setting.

A multidisciplinary team of LLNL researchers has successfully demonstrated a potentially simpler, more accurate way to measure plasma conditions with two laser beams that cross paths.

In an open-access database and with publicly available code, LLNL researchers have simulated and published one million orbits in cislunar space.
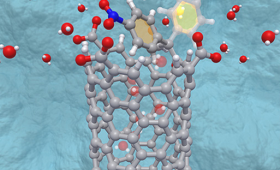
In a recent study, LLNL researchers and collaborators engineered carbon nanotubes with openings that can reversibly open and close depending on pH.


