International Filtration News selected a carbon nanotube (CNT) porin technology developed by Lawrence Livermore researchers and colleagues as one of the top filtration innovations in 2020, featuring it on the cover of issue 6 2020.
Science and Technology
in the News
Science and Technology
in the News
News Center
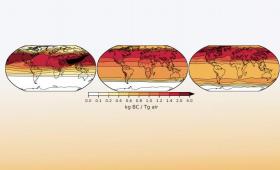
A team of Livermore scientists has modeled the global climatic consequences of a regional nuclear weapons exchange.
This chapter reviews the requirements and design for anti-reflective coatings on laser optics, the sol-gel synthesis process, coating methods and post treatments, coating stability, and laser-damage performance.

A research team has developed a 3D-printed electrode that lessens the problems that occur with gas bubbles that are generated during water electrolysis.

A team of current and former Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and IBM scientists won the annual “Test of Time” award at the 2020 Supercomputing Conference.
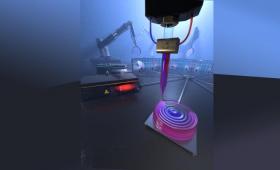
Livermore researchers have used multi-material 3D printing to create tailored gradient refractive index glass optics.
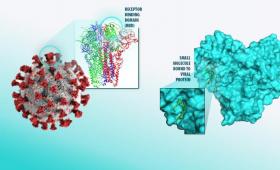
A machine learning model developed by a team of Livermore scientists to aid in COVID-19 drug discovery efforts is a finalist for the Gordon Bell Special Prize for High Performance Computing-Based COVID-19 Research.

Livermore houses four of the world’s 100 most powerful supercomputers, more than any other institution according to the TOP500 list.
The authors review the development of time-resolved, in situ imaging techniques capable of capturing solid–liquid interfacial evolution in metallic alloys.

A long time ago — roughly 4.5 billion years — our sun and solar system formed over the short time span of 200,000 years.


