In 1967, Ronald Reagan, former movie star and then newly-elected governor of California, visited the Lawrence Radiation Laboratory in Livermore, California to tour the facility and become more informed about major ongoing projects, including work on national defense.
Science and Technology
in the News
Science and Technology
in the News
News Center

Livermore, along with the Oak Ridge and Argonne national laboratories and Cray Inc., garnered HPCwire Readers’ and Editors’ Choice Awards for Top Supercomputing Achievement for 2019.

Three teams of Lawrence Livermore scientists, each supported by a Laboratory business development executive, netted regional awards for technology transfer from the Federal Laboratory Consortium.
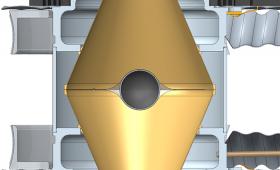
An angular hohlraum named “Frustraum” could become a key to the next stages of ICF research at the National Ignition Facility.

A research team used high‐speed X‐ray imaging to probe subsurface melt pool dynamics and void‐formation mechanisms inaccessible to other monitoring approaches in laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) metal additive manufacturing.

A research team has demonstrated that lead — a metal so soft that it is difficult to machine at ambient conditions — responds similarly to other much stronger metals when rapidly compressed at high pressure.

Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory has won The Laser Institute (LIA)’s inaugural William M. Steen Award for the Academic & Public Sector.

LLNL’s Eyal Feigenbaum received the Alexander Glass Best Oral Presentation Award from SPIE, the international society for optics and photonics.

Livermore researchers have garnered four awards among the top 100 industrial inventions worldwide.

Researchers have discovered that at thermodynamic conditions mimicking that of Earth’s core, argon can react with nickel, forming a stable argon-nickel (ArNi) compound.


