We used 14C birth dating of a main constituent of CAs, that is, collagen type I, as an indicator for biosynthesis and turnover of collagen in CAs in relation to human cerebral arteries to investigate this further.
Journal Covers

Demonstrating the application of nanometer-scale secondary ion mass spectrometry (CAMECA NanoSIMS 50 ion probe) for 3D chemical imaging of individual atmospheric particles without any sample pre-treatment, such as sectioning of particles.

The ability to fabricate 4-level diffractive structures with 1 µm critical dimensions has been demonstrated for the creation of fast (∼f/3.1 at 633 nm) Fresnel zone lenses (FZLs) with >60% diffraction efficiency into the −1 focusing order and nearly complete suppression of 0 and +1 orders.

We describe fully self-consistent time-dependent simulations of radio frequency (RF) generated ion distributions in the ion cyclotron range of frequencies and RF-generated electron distributions in the lower hybrid range of frequencies using combined Fokker–Planck and full wave electromagnetic field solvers.
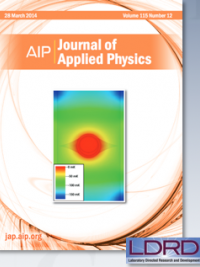
A detailed computation of the temperature profile for liquid hydrogen inside a hollow shell, as is found in inertial confinement fusion research, shows that seeds are likely to form at the equatorial plane of the shell.
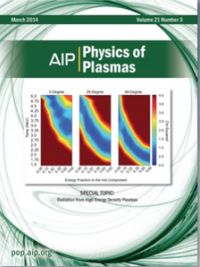
Experiments on the Titan laser at the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory were carried out in order to study the properties of fast electrons produced by high-intensity, short pulse laser interacting with matter under conditions relevant to fast ignition.
Examines models of systems for CO2 capture. A brief survey with a few illustrative examples

Presents the first results from an experimental campaign to measure the atomic ablator-gas mix in the deceleration phase of gas-filled capsule implosions on the National Ignition Facility.

Research team analyzes records of bulk and amino-acid-specific 15N/14N isotopic ratios (δ15N) preserved in the skeletons of long-lived deep-sea proteinaceous corals collected from the Hawaiian archipelago; these isotopic records serve as a proxy for the source of nitrogen-supported export production through time.

Research shows that the interaction of relativistic-intensity, picosecond laser pulses with solid targets is affected by the reflected light through the strong currents and 104 T magnetic fields it produces.


