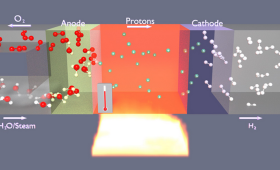
In a new study, published in PRX Energy, LLNL scientists revealed how high operating temperatures could increase electrical leakage in a widely studied fuel cell material.
Science and Technology
in the News
Science and Technology
in the News
News Center

In a recent study, LLNL researchers presented a new method to deposit quantum-dot films on corrugated surfaces.

LLNL researchers are breaking through the barriers of heavy actinides with a streamlined and efficient “serial approach” for the synthesis and analysis of heavy actinide compounds.

In a new study published in Physical Review Letters, a team of researchers from U.S. universities and national laboratories has set stringent limits on the existence and mass of sterile neutrinos.
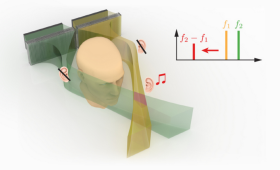
Researchers at Penn State University and LLNL unveil a novel technique that allows sound to be delivered to a precise location, circumventing physical barriers without the need for on-ear devices.
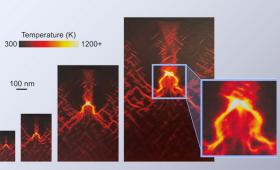
Using LLNL’s Sierra supercomputer, a LLNL team has made significant progress in understanding how microscopic hot spots form in insensitive high explosives.
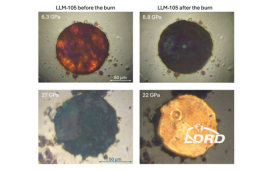
LLNL researchers conducted laser ignition experiments in a diamond anvil cell and employed large scale quantum molecular dynamics simulations to investigate the products of deflagration at high pressures.
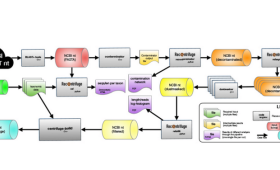
LLNL researchers are working with the National Center for Biotechnology Information's (NCBI) Nucleotide (nt) database to create a vast repository of DNA sequences from across all known species.

Pett-Ridge is among the 471 scientists, engineers and innovators who have been elected American Association for the Advancement of Science 2024 fellows for their scientifically and socially distinguished achievements throughout their careers.

Aleksandr Noy, an LLNL senior research scientist, has been named a 2025 fellow of the Materials Research Society (MRS).