Livermore scientists and colleagues are working on a NASA project to study microorganisms in a Nevada hot spring that could determine whether extraterrestrial life exists.
Science and Technology
in the News
Science and Technology
in the News
News Center
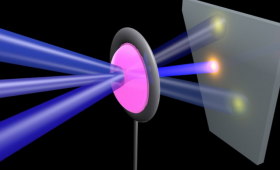
A team of Livermore researchers successfully combined several separate National Ignition Facility lasers into a “superbeam” for the first time.
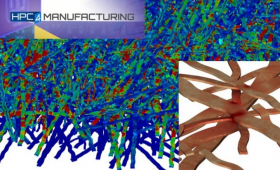
An HPC for Manufacturing project aimed at saving time and money for paper product manufacturers earned an HPC Innovation Excellence Award at the 2017 SuperComputing Conference in Denver.
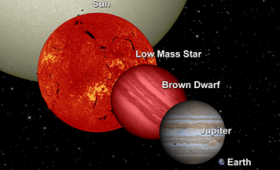
Laboratory scientists have conducted three experiments at the National Ignition Facility to study conditions relevant to matter in brown dwarfs—"failed stars."

An article authored by a team of Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory scientists has characterized how different cell membranes behave.

Livermore researchers have captured seven 2017 R&D 100 awards from R&D magazine's top 100 industrial inventions worldwide.

The melting temperature and equilibrium vapor pressures of 1,4-bis(phenylethynyl)benzene (DEB) do not vary monotonically with the hydrogenation extent.

At the 2017 SuperComputing Conference in Denver, Lawrence Livermore researchers took home two HPCwire Editor’s Choice awards for their work in applying high-performance computing (HPC) to solve complex challenges.

The American Heart Association (AHA) and Lawrence Livermore have formed a strategic business partnership to overcome the burden of drug discovery, cost, and access.

In this podcast, the Radio Free HPC team reviews the latest TOP500 list in front of a live audience in Denver at SC17.


