Massive compressive shearing forces generated by the tidal pull of Jupiter-like planets on their rocky ice-covered moons may form a natural reactor that drives simple amino acids to polymerize into larger compounds.
Science and Technology
in the News
Science and Technology
in the News
News Center

Join Dr. Leland Ellison as he shares a full-length Fun with Science presentation from LLNL’s Discovery Center.
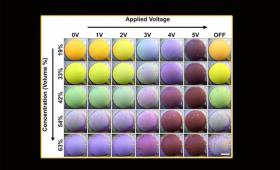
Livermore researchers are perfecting a technology called reversible electrophoretic deposition for high-contrast wearable displays.
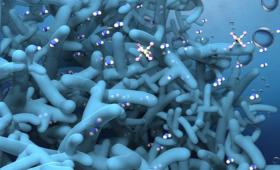
Mimicking the structure of the kidney, a team has created a three-dimensional nanometer-thin membrane that breaks the permeance-selectivity trade-off of artificial membranes.
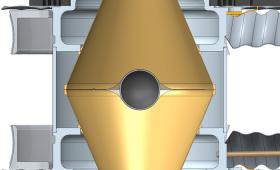
Initial NIF experiments using a full-scale version of the Frustraum hohlraum have produced nearly round inertial confinement fusion implosions and more laser-induced energy absorption.
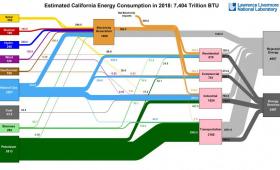
Livermore has updated its energy flow charts to include state-by-state energy use for 2015-2018.
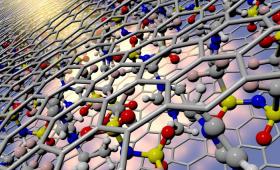
Livermore scientists coupled X-ray experiments with high-fidelity simulations to investigate a widely used family of ionic liquids confined in carbon nanopores typically used in supercapacitors.

The most advanced and comprehensive analysis of climate sensitivity undertaken has revealed with more confidence than ever how sensitive the Earth’s climate is to carbon dioxide.

Livermore physicist Yuan Shi has earned the American Physical Society’s Marshall N. Rosenbluth Outstanding Doctoral Thesis award for his work in plasma physics.

Three scientists from Livermore are recipients of the 2020 John Dawson Award for Excellence in Plasma Physics Research from the American Physical Society.


