The National Ignition Facility is highlighted in a recent assessment of the state and future of plasma science by the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering and Medicine.
Science and Technology
in the News
Science and Technology
in the News
News Center
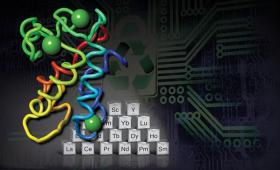
Researchers have designed a new process, based on a naturally occurring protein, that could extract and purify rare earth elements (REE) from low-grade sources.

In the summer of 1956, a U.S. Navy-sponsored study (Project Nobska) on anti-submarine warfare was held at Woods Hole, Massachusetts.

Researchers use a multivariate approach to identify two distinct externally forced fingerprints from multiple ensembles of Earth system model simulations.

Research led by Livermore scientists has identified two signatures or “fingerprints” that explain why arid conditions are spreading worldwide.

This video summarizes some of the work that Lawrence Livermore researchers and staff are doing to respond to the COVID-19 epidemic.
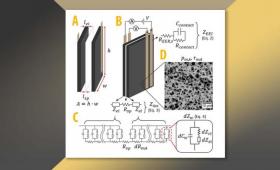
LLNL scientists have provided a comprehensive practical overview of a capacitive deionization cell's resistive components both experimentally and theoretically.
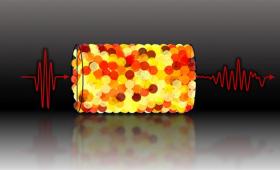
Researchers find principles underlying velocity scaling and dispersion in wave transmission through grainy particle arrangements.

Livermore's technology transfer team has opened up multiple fronts to aid the nation’s efforts against the SARS-CoV-2 virus that causes COVID-19.

Two Livermore scientists, Federica Coppari and Erin Nuccio, are recipients of the Department of Energy’s Office of Science Early Career Research Program award.


