Renowned Livermore atmospheric scientist Ben Santer has been honored with the American Geophysical Union’s 2020 Bert Bolin Award.
Science and Technology
in the News
Science and Technology
in the News
News Center

An LLNL team solved a mystery of metallurgy by simulating the metal hardening process.
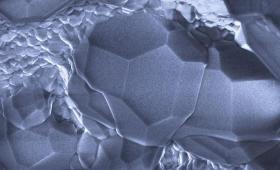
A multi-institutional research team synthesized methane hydrate with sediments to determine the electrical conductivity of the mixtures.

In 1963, a comprehensive, long-range program dealing with the sources and biological effects of human-made radiation was established by the Atomic Energy Commission (AEC) at the Lawrence Radiation Laboratory, Livermore.

In this experiment, “elephant toothpaste” is made by the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide using a catalyst to facilitate an otherwise invisible chemical reaction. H202 is decomposed in a graduated cylinder by adding a scoop of potassium iodide. Soap is added to make the mixture foam and food coloring is used to add color and the effect of foaming toothpaste.

Experiments with ultra-cold liquid nitrogen demonstrate states of matter, such as solids, liquids and gases, and phase transitions between these states using everyday items. A large CO2 balloon is compressed inside a tiny beaker by freezing the gas into dry ice. Then, a fluffy marshmallow is submerged in liquid nitrogen and shattered into tiny pieces.
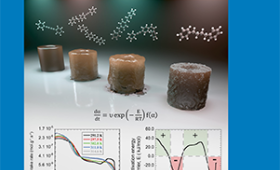
To make more accurate predictions of the performance of a pelletized system, researchers used isothermal–isobaric and dynamic pressure experiments to test hydrogen uptake using constant pressure and at a higher temperature range than previous tests.

Livermore researchers have created carbon nanotube pores that are so efficient at removing salt from water they are comparable to commercial desalination membranes.

Staff Scientist Félicie Albert has been elected a Kavli Fellow of the U.S. National Academy of Sciences.

A research team measures water and ion permeation through 0.8-nm-diameter carbon nanotube porins, finding them comparable to commercial desalination membranes.


