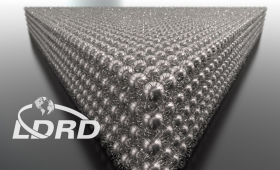
A Livermore-led team studies the nanocrystal assembly process in silver.
Science and Technology
in the News
Science and Technology
in the News
News Center

For the first time, researchers have developed a way to determine how many cancer cells it takes to initiate a tumor in another part of the body.

Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory researchers Tayyab Suratwala and Jay Dawson have been named fellows by The Optical Society of America.

Four Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory scientists have been selected as 2018 fellows of the American Physical Society.

A team of theorists from Livermore has solved a long-standing puzzle in the nucleation of a high-pressure phase of ice known as ice VII.

The Nobel Prize-winning research by Donna Strickland, a former LLNL staff scientist as instrumental in the Laboratory’s development of a series of groundbreaking short-pulse, high-energy laser systems.

Take a peek inside the National Ignition Facility, the world’s largest and most energetic laser, to see how we develop and execute some of the most complex experiments conducted anywhere.
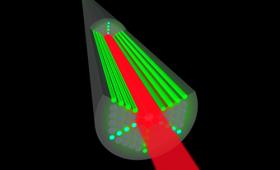
LLNL has received two significant awards that will help advance the next stage of developing fiber-optic cable technology.
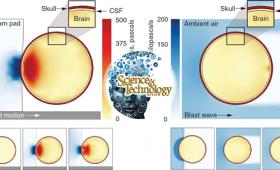
Livermore simulations are helping scientists understand and prevent traumatic brain injury (TBI).
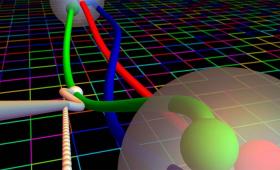
A Livermore–Berkeley team is a finalist for the prestigious 2018 Gordon Bell Award, one of the world’s top honors in supercomputing.