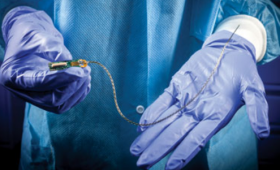
A new study compares drug responses in the brains of rodents to drug responses of brain cells cultured in Livermore-developed “brain-on-a-chip” devices
Science and Technology
in the News
Science and Technology
in the News
News Center
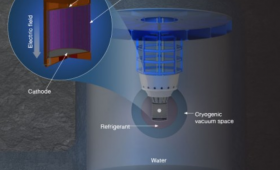
Livermore participates in an effort to observe extremely rare neutrinoless double-beta decay.

Lawrence Livermore magnetic fusion physicist Max Fenstermacher has been awarded the 2018 John Dawson Award for Excellence in Plasma Physics Research from the American Physical Society.

A firefighter enters a burning office building followed by several drones, searching for people in need of rescue. The drones scatter in different directions, moving down corridors and systematically scanning rooms.
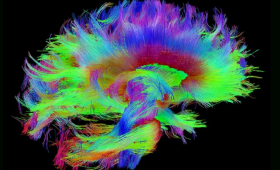
Livermore will use high-performance computing in partnership with other national labs and universities to improve the scientific understanding and treatment of traumatic brain industry.

The L3-HAPLS advanced petawatt laser system has been declared fully integrated and operational at the ELI Beamlines Research Center.

Modeling the effects of shock pressure and pore morphology on hot spot mechanisms in HMX

Lawrence Livermore’s next-generation supercomputer, Sierra, is the third-fastest computing system in the world, according to the TOP500 list.

Tammy Ma, a plasma physicist at Lawrence Livermore, has been named a recipient of the prestigious Department of Energy Office of Science Early Career Research Program.