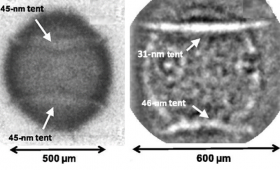
Livermore scientists are working to mitigate the adverse effects on National Ignition Facility implosion performance of the gossamer-thin membranes known as “tents” that support the target capsule in the hohlraum.
Science and Technology
in the News
Science and Technology
in the News
News Center

LLNL's John Nasstrom received the NNSA Administrator’s Distinguished Service Gold Award.

New research provides a theoretical explanation for why self-organized fluid flows called zonal jets or “zonal flows” can be suppressed by the presence of a magnetic field.

Lawrence Livermore and its partners are using microbes to convert carbon dioxide directly to renewable natural gas.

Livermore scientists are collecting, archiving, and documenting climate data sets to support coordinated climate modeling activities.

The Food and Drug Administration has approved the use of a medical device in humans partly developed at Livermore.

Lawrence Livermore chemist Dawn Shaughnessy, whose team helped discover six new elements on the periodic table, has been elected a fellow of the American Chemical Society.
For the first time, scientists from Lawrence Livermore and five other organizations have shown that human influences significantly impact the size of the seasonal cycle of temperature in the lowest layer of the atmosphere.

Nearly four decades of global temperature data collected by satellites reveal the atmospheric fingerprint of climate change.

Retired physicist Bruce Cohen has been selected as the recipient of the 2018 IEEE Nuclear and Plasma Sciences Society’s Charles K. Birdsall Award .