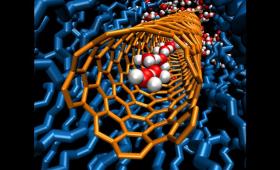
Multi-institutional group of researchers examines single digit nanopores.
Science and Technology Highlights

By comparing observations to large ensembles of climate model simulations, scientists can now better isolate when human-caused climate change was first identifiable in observations.

The Large Synoptic Survey Telescope will take photos using optical assemblies designed by Lawrence Livermore researchers.

Scientists are going to the microscale to study the diverse characteristics of nuclear fuel pellets that could improve nuclear forensic analysis.

Researchers have developed a technology that can remove nitrate from water selectively.

U.S. Secretary of Energy Rick Perry and Sandy Weill, founder of the Weill Family Foundation, signed a memorandum of understanding to formally initiate a public-private partnership for artificial intelligence (AI), neurological disorders and related subjects.

An international team of researchers has developed a new algorithm for solving polynomial systems of equations using a type of quantum computer called a “quantum annealer.”
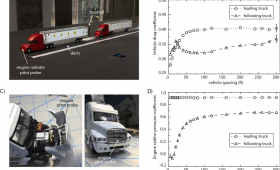
Since the late 1990s, LLNL has played a significant role in improving the fuel economy of class-8 heavy vehicles through enhanced aerodynamics.

The Department of Energy, National Nuclear Security Administration, and the Laboratory announced the signing of contracts with Cray Inc. to build the NNSA’s first exascale supercomputer, “El Capitan.”
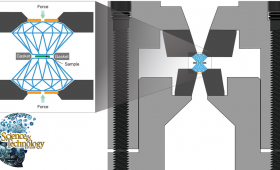
A new design for diamond anvil cells helps scientists examine materials of interest.