Livermore cosmochemists are among those who will analyze the Apollo 17 samples sealed 50 years ago to study the geologic history of the site where the rocks were collected.
Science and Technology Highlights

Livermore is developing machine learning tools for applications beyond standard commercial and consumer applications

Climate scientists at Livermore announced the release of new data sets that will provide fresh insights into past and future climate change.
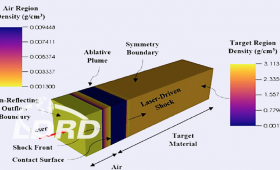
Researchers have discovered an efficient mechanism for laser ablation that could help pave the way to the use of less costly lasers in many industrial laser processing applications.

An international team has found the answer to a 50-year-old puzzle that explains why beta decays of atomic nuclei are slower than expected.

Investigators have found a technique to reduce the uncertainty in predicting future change.
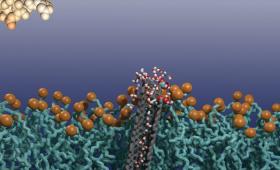
Livermore researchers have developed a new biological sensor that could help clinicians better diagnose cancer and epilepsy.

Livermore launched a new initiative focused on sharing solutions with local communities to help them develop a sustainable, resilient and affordable energy infrastructure.

A research team has learned how the digestive system of a wood-eating beetle serves as a natural mini-reactor for biofuel production.
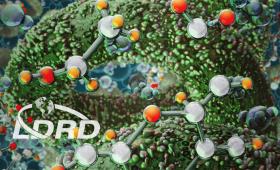
Researchers have 3D printed live cells that convert glucose to ethanol and carbon dioxide gas (CO2), demonstrating a technology that can lead to high biocatalytic efficiency.


