Livermore scientists have developed a promising drug that permeates the blood-brain barrier.
Science and Technology Highlights

The LLNL Independent Diagnostic Scoring System (LIDSS) measures crucial impact parameters during intercontinental ballistic missile tests.
Comets impacts may have produced nitrogen-containing aromatic structures that are likely constituents of polymeric biomaterials.
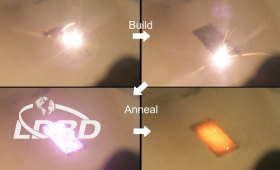
Researchers have developed a technique to reduce residual stress in metal 3D printed parts using laser diodes.

Nuclear chemist Dawn Shaughnessy joined a team of scientists from Lawrence Livermore and Russia that discovered five elements from 1989 to 2010.

Livermore’s Lassen joined its companion system Sierra in the top 10 of the TOP500 list of the world’s most powerful supercomputers.

Researchers have identified a molecular mechanism in bacteria that can overcome a key gap in biofuel and biochemical production processes.

Researchers have elucidated the transition in the chemical bonding mechanism that enables the data storage in phase-change materials.
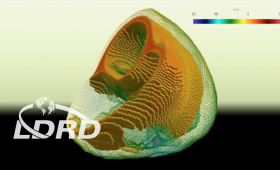
Livermore researchers have successfully optimized a code that models the human heartbeat for next-generation, graphics processing unit (GPU)-based supercomputers.



