Livermore has developed a new additive manufacturing process for materials used to train dogs for explosives detection.
Science and Technology
in the News
Science and Technology
in the News
News Center

The rocks in Oman remove planet-warming carbon dioxide from the air and turn it to stone. In theory, these rocks could store hundreds of years of human emissions of CO2.

Iron-silicon alloys have been compressed to unprecedented pressures equal to the center of a three-Earth-mass extrasolar planet.
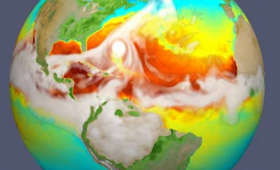
A new earth modeling system has been unveiled with weather-scale resolution that uses advanced computers to simulate Earth’s variability.

Livermore researchers have mapped out how CO2 might be captured from existing U.S. ethanol biorefineries and stored underground.

For the first time, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory has issued state-by-state energy and water flow charts in one location.

A team of researchers has provided the first experimentally based mass-radius relationship for a hypothetical pure iron planet at super-Earth core conditions.

A team of researchers has provided the first experimentally based mass-radius relationship for a hypothetical pure iron planet at super-Earth core conditions.
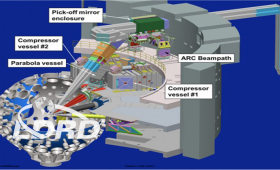
An international team of researchers has created a powerful new source of protons at the National Ignition Facility.



