LLNL flagship exascale machine El Capitan maintained its status as the fastest supercomputer on the planet — claiming the No. 1 spot on three of the most prestigious high-performance computing (HPC) rankings.
Science and Technology
in the News
Science and Technology
in the News
News Center

LLNL Deputy Director for Science and Technology Patricia Falcone was presented with the AI Honors in Public Science award at the inaugural AI Honors Gala on June 3 at the Waldorf Astoria Hotel in Washington, D.C.
LLNL researchers and collaborators are using artificial intelligence and machine learning (AI/ML) to try to find amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) treatments.
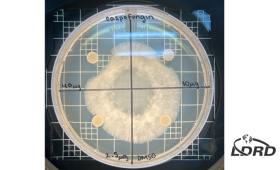
In a study published in the Journal of Microbiological Methods, LLNL researchers combined and refined two established techniques into a new method to screen chemicals for their ability to kill filamentous fungi.
In a new study, published in Analytical Chemistry, LLNL researchers develop a fast and simple approach to screen proteins and their binding properties.

A more than month-long field experiment by an LLNL seismologist demonstrates that a new technology could offer a major breakthrough in seismology.
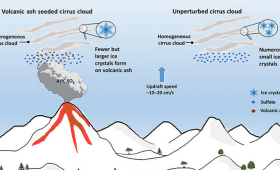
In a study published in Science Advances, LLNL researchers analyzed 10 years of satellite data to determine that volcanic ash particles can trigger cloud formation.
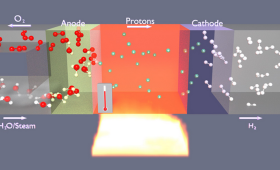
In a new study, published in PRX Energy, LLNL scientists revealed how high operating temperatures could increase electrical leakage in a widely studied fuel cell material.

Five LLNL postdoctoral researchers have been selected to participate in the prestigious 2025 Lindau Nobel Laureate Meetings.

In a recent study, LLNL researchers presented a new method to deposit quantum-dot films on corrugated surfaces.

