Science and Technology
in the News
Science and Technology
in the News
News Center

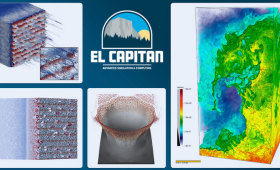
LLNL researchers model extreme physical events with unprecedented resolution, realism and speed.

LLNL researchers analyzed asteroid material to show that its elements reflect the early composition of the solar system.

LLNL researchers employed an AI-driven model to predict fusion ignition days ahead of the historic 2022 shot.

LLNL physicist Cole Pruitt has been awarded the 2025 Facility for Rare Isotope Beams (FRIB) Achievement Award for Early Career Researchers in theoretical nuclear physics.
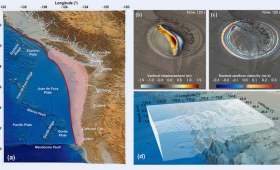
LLNL scientists have helped develop an advanced, real-time tsunami forecasting system that could dramatically improve early warning capabilities.

At a conference held this summer, the American Association for Crystal Growth (AACG) recognized LLNL scientist Luis Zepeda-Ruiz with its Gentile Service Award.
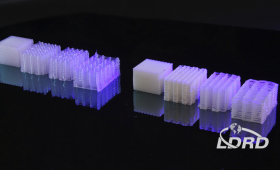
LLNL scientists and collaborators have created a new class of programmable soft materials that can absorb impacts like never before.

Optimax Space Systems have signed a Cooperative Research and Development Agreement (CRADA), expanding production of LLNL’s next-generation space domain awareness technology.


