Science and Technology Highlights

In collaboration with an international team, LLNL scientists looked at the isotopic composition of oxygen, carbon and manganese-chromium in two asteroid particles to help determine the source of the water and timing of the chemical reactions


Skywing, a new software developed at LLNL, provides scientists working to protect the nation’s critical infrastructure with a high-reliability, real-time software platform for collaborative autonomy applications.

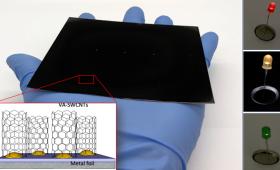
Researchers have created vertically aligned single-walled carbon nanotubes that could be a boon for energy storage and the electronics industry.

An international team reports the oldest ancient environmental DNA record to date, describing the rich plant and animal assemblages of the Kap København Formation in north Greenland

In new research published in Physical Review B, LLNL scientists report on a series of X-ray diffraction experiments on five metals dynamically compressed to 600 GPa (6,000,000 atmospheres of pressure).

