Livermore researchers are using the third generation of early access machines to port codes over to the future exascale system El Capitan.
Science and Technology Highlights

Livermore scientists have devised a method to fabricate all-solid-state lithium metal batteries.

Livermore scientists develop a copper–titanium catalyst to mitigate use of precious metals.

Members of Livermore’s DART spacecraft discuss being present at mission control during he world’s first planetary defense technology demonstration.

John Clauser, an experimental physicist who spent a decade at Livermore, has been awarded the 2022 Nobel Prize in Physics, along with French scientist Alain Aspect and Austrian scientist Anton Zeilinger.

An international research team has succeeded in studying the chemical properties of the superheavy element flerovium — element 114.

A new paper led by LLNL walks through a detailed “dress rehearsal” for interpretation of the DART asteroid mission's experiment’s data.

An international team has determined that one specific particle on the asteroid Ryugu can shed light on the unaltered initial materials from its parent body.
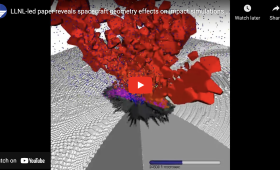
Livermore researchers contribute simulation expertise to NASA’s DART planetary-defense tech-demo mission.

Magnesium at 10 million times atmospheric pressure adopts fundamentally new chemical and structural behavior.


