Research suggests that immune responses could be bolstered by drugs to help people recover from brain infections caused by an emerging pathogen, according to studies of the emerging pathogen Rift Valley fever virus.
Science and Technology Highlights

A record high-laser-energy NIF target shot on Sept. 19 produced about 1.2 million joules of fusion energy yield.

New research suggests that grassland viral communities are highly spatially stratified across just a single field.

A new National Ignition Facility Discovery Science campaign is designed to simulate the type of photoionized plasma found in accretion disks and the surrounding stellar wind.

To transform the way energy is collected, stored, and used, the Office of Basic Energy Sciences (BES) awarded Livermore and collaborators three energy-focused projects.
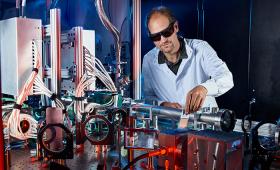
Spiral phase mirrors, when incorporated into a laser system, will enable scientists to “twist” the laser light and generate an optical vortex.

A five-year microbial study of the International Space Station and its astronauts by Lawrence Livermore and NASA researchers has found that the ISS habitat is safe for its residents.
Livermore scientists are scaling up the production of vertically aligned single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNT) that could revolutionize a diverse set of commercial products.

Livermore researchers are using the third generation of early access machines to port codes over to the future exascale system El Capitan.

Livermore scientists have devised a method to fabricate all-solid-state lithium metal batteries.


