Science and Technology Highlights

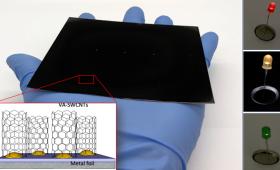
Researchers have created vertically aligned single-walled carbon nanotubes that could be a boon for energy storage and the electronics industry.

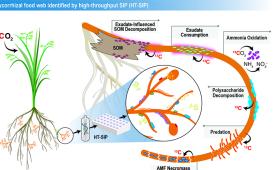
An international team reports the oldest ancient environmental DNA record to date, describing the rich plant and animal assemblages of the Kap København Formation in north Greenland

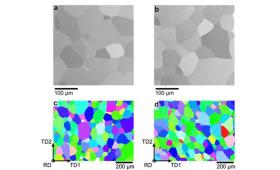
In new research published in Physical Review B, LLNL scientists report on a series of X-ray diffraction experiments on five metals dynamically compressed to 600 GPa (6,000,000 atmospheres of pressure).

LLNL scientists have developed a new technique to analyze fentanyl in human blood and urine samples that could aid work in the fields of medicine and chemical forensics.