To help the United States fight the COVID-19 pandemic, Lawrence Livermore did what it does best: quickly bring together interdisciplinary teams and diverse technologies to address urgent national challenges.
Science and Technology Highlights

A research team has created machine learning models that can predict molecules’ crystalline properties from their chemical structures alone, such as molecular density.
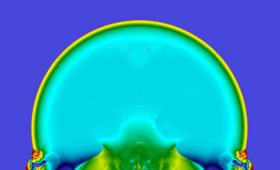
A Livermore team has taken a closer look at how nuclear weapon blasts close to the Earth’s surface create complications in their effects and apparent yields.

Researchers describe how a laser-plasma system can be tuned to produce large and measurable changes in the group velocity of light.

Researchers have developed a light-activated switch that, if fully deployed, could reduce carbon emissions by more than 10 percent.

The Livermore-led VisIt visualization and analysis tool has supported scalable, high-quality evaluation of simulation results for over 20 years.

Scientists have revealed experimental evidence that helium rain is possible over a range of pressure and temperature conditions expected to occur inside Jupiter and Saturn.

With a number of Department of Energy incentives and funding streams, Lawrence Livermore’s research commercialization efforts are changing the world and paving the way for technology’s next big thing.

Laboratory researchers have produced and refined the lowest-density gold foam aerogel ever made—a significant breakthrough in nanoscale materials engineering.
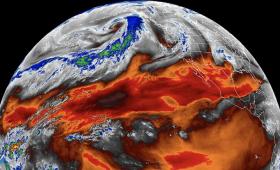
New research shows that satellite measurements of the temperature of the troposphere may have underestimated global warming over the last 40 years.