From studying radioactive isotope effects to better understanding cancer metastasis, the Laboratory’s relationship with cancer research endures some 60 years after it began.
Science and Technology Highlights

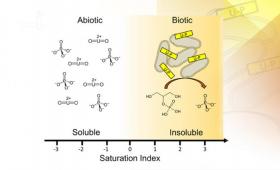
Researchers study protist–plant relationships to understand the role of protists in the rhizosphere.

Global warming causes low-level clouds over the oceans to decrease, leading to further warming.

Thin-film electrodes developed at Lawrence Livermore have been used in human patients at the University of California, San Francisco, generating never-before-seen recordings of brain activity in the hippocampus.
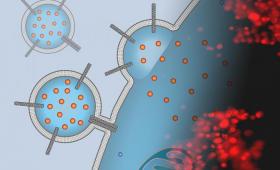
A research team has used carbon nanotubes to enable direct drug delivery from liposomes through the plasma membrane into the cell interior.

The Center for Non-Perturbative Studies of Functional Materials under Non-Equilibrium Conditions advances high-performance computing software to support novel materials discovery.

Scorpius, a multi-lab project to advance stockpile stewardship, will yield an unprecedented experimental tool powered by Livermore technology.
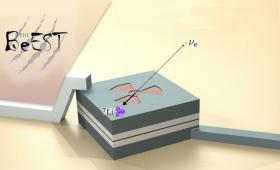
A research team has demonstrated the power of using nuclear decay in high-rate quantum sensors in the search for sterile neutrinos.

Livermore researchers develop a system to help analysts find evidence of nuclear weapons proliferation using open-source information.