New materials made with carbon nanotube composites and a special thin polymer layer protect first responders from chemical and biological threats without sacrificing breathability and comfort.
Science and Technology Highlights

A new take on an additive manufacturing tool may be the key to capturing waste heat from manufacturing processes and converting it to electricity.

Livermore technology transfer and private-sector partnerships played an important role in fighting the COVID-19 pandemic.

A research team leverages the power of 3D printing to improve the performance of electrochemical reactors used to convert carbon dioxide (CO2) to useful energy sources, chemicals and material feedstocks.

Just a few bacterial groups found in ecosystems across the planet are responsible for more than half of carbon cycling in soils.
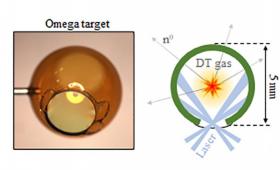
Livermore scientists have demonstrated a new geometry for a neutron source platform for the National Ignition Facility.
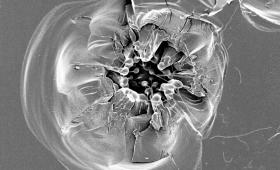
Livermore researchers have developed and are now installing high-quality fused silica debris shields to increase the National Ignition Facility’s shot rate.

Researchers have developed a new machine learning-based approach for modeling inertial confinement fusion experiments that results in more accurate predictions of National Ignition Facility shots.
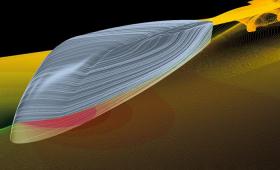
Livermore engineers have demonstrated aerodynamically integrated energy-efficient vehicle shapes for heavy vehicles.

Researchers have developed a groundbreaking method for transporting liquids and gases using 3D-printed lattice design.


