The White House announced the launch of the COVID-19 High Performance Computing Consortium that can significantly advance the pace of scientific discovery in the fight to stop the virus.
Science and Technology Highlights
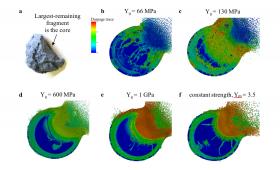
Planetary defense researchers at Lawrence Livermore continue to validate their ability to accurately simulate how they might deflect an Earth-bound asteroid.

Scientists looked at how much carbonyl sulfide comes from forest fires and other burning biomass to measure photosynthesis.

Monitoring antineutrinos emitted by nuclear reactors could help detect illicit production of plutonium.

LLNL and its partner laboratories and universities have designed and built an extensive suite of more than a dozen nuclear diagnostics for the National Ignition Facility.

Lawrence Livermore, Hewlett Packard Enterprise, and Advanced Micro Devices Inc. (AMD) announced the selection of AMD as the node supplier for El Capitan, projected to be the world’s most powerful supercomputer when it is fully deployed in 2023.

A multi-institutional collaboration explored current understanding of the physical processes that can drive flash droughts.

Researchers have observed the shock melting and refreezing of a metal (zirconium) at the picosecond scale.

Tropical glaciers in Africa and South America began their retreat simultaneously at the end of the last ice age about 20,000 years ago.
Scientists have tracked down a potential target for new drugs against sleeping sickness.


