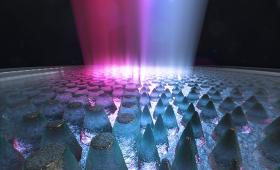
Lawrence Livermore scientists have discovered a new method to add an antireflective metasurface (ARMS) layer on laser optics glass that’s so durable, it can survive getting “smooshed.”
Science and Technology Highlights

A paper describing the design and performance of a workhorse NIF experimental platform known as TARDIS (target diffraction in situ) was a featured article in a recent edition of the journal Review of Scientific Instruments.
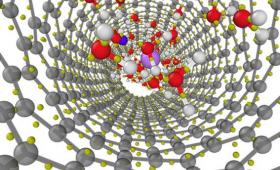
A multi-institutional research team explored how the structure and electronic properties of liquid water can be affected by the presence of ions and nanoconfinement
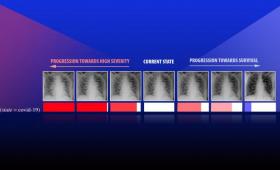
A team led by a Livermore computer scientist proposes a novel deep learning approach aimed at improving the reliability of models designed for predicting disease types from diagnostic images.
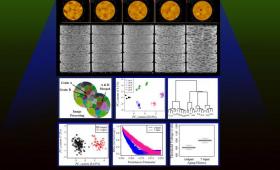
Scientists take a step forward in the design of future materials with improved performance by analyzing microstructure using AI.

Livermore engineers formed an ad hoc, rapid response team that has tested more than a dozen novel, 3D-printed nasal swab designs to aid in COVID-19 response.
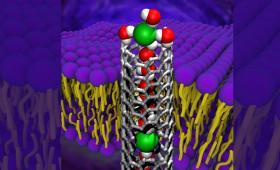
Livermore researchers determined how negatively charged ions squeeze through a carbon nanotube 20,000 times smaller than a human hair.
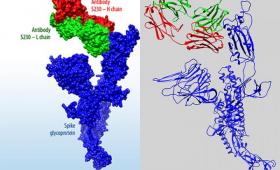
To help accelerate discovery of therapeutic antibodies or antiviral drugs for SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, Lawrence Livermore has launched a searchable data portal to share its COVID-19 research with scientists worldwide and the general public.
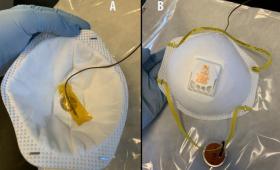
Livermore researchers are studying ways to safely and rapidly remove viral threats from N95 respirators so they can be reused.

A Livermore team developed machine learning tools that extract and structure information from the text and figures of nanomaterials articles.