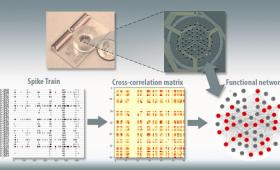
LLNL researchers have developed a way to computationally model the activity and structures of neuronal communities as they grow and mature on the device over time.
Science and Technology Highlights

Following weeks of prototyping, Livermore is partnering with private industry to mass-produce a simple mechanical ventilator developed for COVID-19 patients that has been authorized for emergency use by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.

Livermore researchers are working with other Department of Energy national labs on technologies to improve the speed and accuracy of tests for COVID-19.
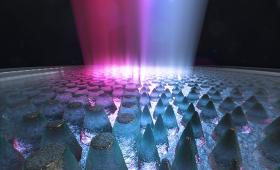
Lawrence Livermore scientists have discovered a new method to add an antireflective metasurface (ARMS) layer on laser optics glass that’s so durable, it can survive getting “smooshed.”

A paper describing the design and performance of a workhorse NIF experimental platform known as TARDIS (target diffraction in situ) was a featured article in a recent edition of the journal Review of Scientific Instruments.
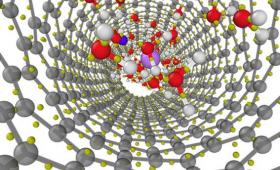
A multi-institutional research team explored how the structure and electronic properties of liquid water can be affected by the presence of ions and nanoconfinement
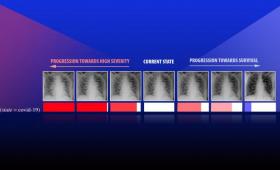
A team led by a Livermore computer scientist proposes a novel deep learning approach aimed at improving the reliability of models designed for predicting disease types from diagnostic images.
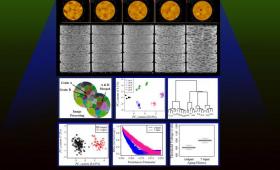
Scientists take a step forward in the design of future materials with improved performance by analyzing microstructure using AI.

Livermore engineers formed an ad hoc, rapid response team that has tested more than a dozen novel, 3D-printed nasal swab designs to aid in COVID-19 response.
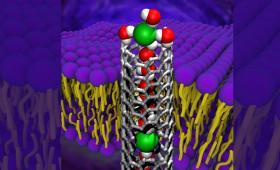
Livermore researchers determined how negatively charged ions squeeze through a carbon nanotube 20,000 times smaller than a human hair.