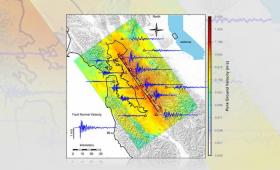
A Livermore team has published new supercomputer simulations of a magnitude 7.0 earthquake on the Hayward Fault, the highest-ever resolution ground motion simulations on this scale.
Science and Technology Highlights
A research team has combined machine learning, 3D printing, and high-performance computing simulations to accurately model blood flow in the aorta.
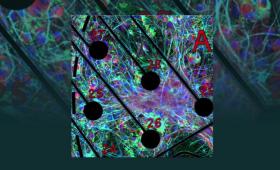
Livermore researchers have increased the complexity of neuronal cultures grown on microelectrode arrays.

Researchers at Livermore and an international team of collaborators have developed an experimental capability for measuring the basic properties of matter at the highest pressures thus far achieved in a controlled laboratory experiment.

Massive compressive shearing forces generated by the tidal pull of Jupiter-like planets on their rocky ice-covered moons may form a natural reactor that drives simple amino acids to polymerize into larger compounds.
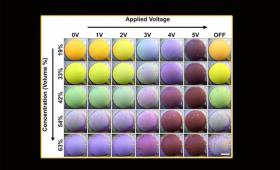
Livermore researchers are perfecting a technology called reversible electrophoretic deposition for high-contrast wearable displays.
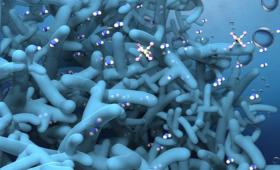
Mimicking the structure of the kidney, a team has created a three-dimensional nanometer-thin membrane that breaks the permeance-selectivity trade-off of artificial membranes.
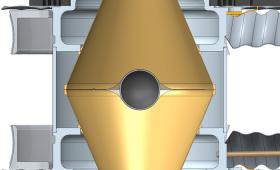
Initial NIF experiments using a full-scale version of the Frustraum hohlraum have produced nearly round inertial confinement fusion implosions and more laser-induced energy absorption.
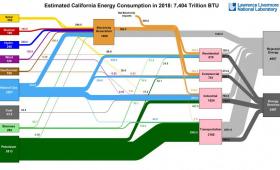
Livermore has updated its energy flow charts to include state-by-state energy use for 2015-2018.
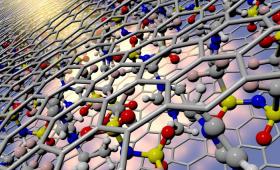
Livermore scientists coupled X-ray experiments with high-fidelity simulations to investigate a widely used family of ionic liquids confined in carbon nanopores typically used in supercapacitors.