Livermore scientists and engineers are combining mechanical computing with 3D printing as part of an effort to create “sentient” materials that can respond to changes in their surroundings.
Science and Technology Highlights
New research shows that synthetic solid-state nanopores can have finely tuned transport behaviors much like the biological channels that allow a neuron to fire.
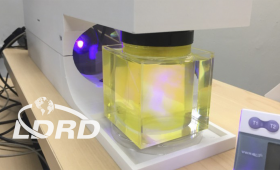
Researchers have developed a new high-speed 3D printing method called Computed Axial Lithography.
Livermore scientists have been researching and developing quantum systems for a decade

Livermore scientists are developing software to protect the electric grid from cyberattack

Virtual reality technology finds real-world applications at the National Ignition Facility.
A Livermore team has taken a key step toward creating a commercial tool that utilities could use to modernize the grid.

The Sierra snowpack will decline in years to come because of climate change effects.