Livermore's Seismic Cooperation Program helps at-risk countries improve earthquake monitoring capabilities, implement suitable seismic building codes, and plan disaster response.
Science and Technology Highlights
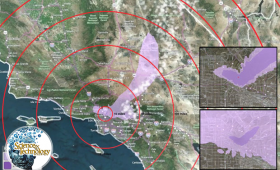
A team of Laboratory engineers, computer scientists, and health physicists have developed a planning resource that can assist local governments in determining the best actions to take following the detonation of an improvised nuclear device.
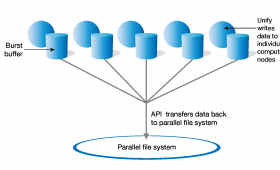
Livermore develops software to reduce performance drag caused by input/output (I/O) workloads.
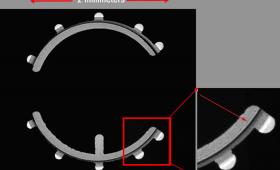
LLNL target fabrication scientists have found a way to make an already hair-thin layer of frozen inertial confinement fusion fuel even slimmer.
The Discovery Science Program has spun off a wealth of benefits to the world’s largest and highest-energy laser system.

Sierra, Livermore’s newest supercomputer, rose to second place on the list of the world’s fastest computing systems, the TOP500 List.

Livermore will accept delivery of Corona, a new unclassified high-performance computing cluster.

Livermore scientists are working to determine the risk to the grid from a cyberattack.
Livermore has won five Technology Commercialization Fund grants from the Department of Energy.

Researchers at Livermore and the University of California, Santa Cruz have created 3D-printed supercapacitor electrodes capable of achieving record-breaking performance.