Experiments using a hohlraum shaped like a rugby ball have significantly boosted the amount of laser-induced energy absorbed by an inertial confinement fusion fuel capsule.
Science and Technology Highlights

Lawrence Livermore nuclear scientists for the first time have accurately predicted the properties of polarized thermonuclear fusion.

New research reveals that the radioactive isotope zirconium-88 is an excellent neutron absorber.
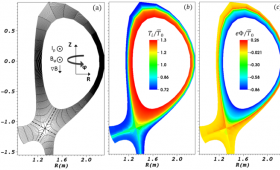
LLNL's Center for Applied Scientific Computing collaborates with its fusion researchers.
Livermore and University of Vermont researchers are exploring how deep reinforcement learning can discover therapeutic drug strategies for sepsis.
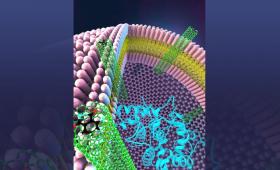
Livermore scientists have created polymer-based membranes that mimic the architecture of cellular membranes.

A newly created two-micron-diameter fill tube solves a problem in inertial confinement fusion experiments.
Scientists have discovered an unusual new type of phase transformation in the transition metal zirconium.

Livermore researchers have introduced a new class of metamaterials that can nearly instantly respond and stiffen 3D-printed structures when exposed to a magnetic field.

The Laboratory has delivered a first-of-its-kind, high-power, fiber-based sodium laser guide star to the University of California, Santa Cruz.