Livermore innovations in lasers made laser peening, using intense laser light to improve the quality of a material, a commercialization success story.
Science and Technology Highlights

Livermore has developed a new additive manufacturing process for materials used to train dogs for explosives detection.

Iron-silicon alloys have been compressed to unprecedented pressures equal to the center of a three-Earth-mass extrasolar planet.

Livermore researchers have mapped out how CO2 might be captured from existing U.S. ethanol biorefineries and stored underground.
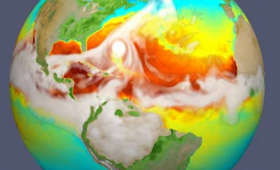
A new earth modeling system has been unveiled with weather-scale resolution that uses advanced computers to simulate Earth’s variability.

For the first time, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory has issued state-by-state energy and water flow charts in one location.

A team of researchers has provided the first experimentally based mass-radius relationship for a hypothetical pure iron planet at super-Earth core conditions.
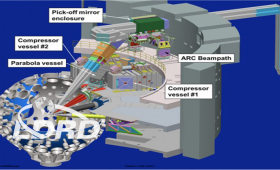
An international team of researchers has created a powerful new source of protons at the National Ignition Facility.

The Axion Dark Matter Experiment (ADMX) unveiled a new result in Physical Review letters: it has achieved the necessary sensitivity to “hear” the telltale signs of dark matter axions.

Livermore researchers have developed and tested an optical telescope system that can be used for Earth and space observation.


