The Axion Dark Matter Experiment (ADMX) unveiled a new result in Physical Review letters: it has achieved the necessary sensitivity to “hear” the telltale signs of dark matter axions.
Science and Technology
in the News
Science and Technology
in the News
News Center

Livermore researchers have developed and tested an optical telescope system that can be used for Earth and space observation.

A research team is using machine learning to track the progression of sepsis, a potentially life-threatening condition characterized by an extreme reaction to infection.

For the first time, researchers at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory have successfully 3D-printed optical-quality glasses, on par with commercial glass products.
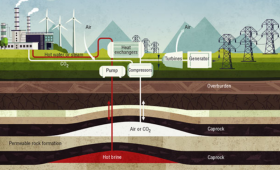
The Earth Battery uses multiple fluids to store energy as pressure and heat underground.
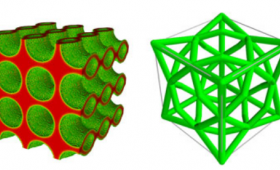
The Laboratory’s Center for Design Optimization is working to fundamentally transform how engineers design complex parts and systems to be additively manufactured.

The Department of Defense and other U.S. agencies perform national-security-related experiments on the National Ignition Facility.

Lawrence Livermore's Target Fabrication Team builds tiny targets that illuminate big questions at the National Ignition Facility.
Lawrence Livermore will lead a new international multi-laboratory and university collaboration for nonproliferation research.

What are nations like North Korea and Iran really doing at nuclear reactors that are out of sight?
Someday, wispy subatomic particles known as antineutrinos could provide a clear view of what countries with illicit nuclear weapons programs are trying to hide.


