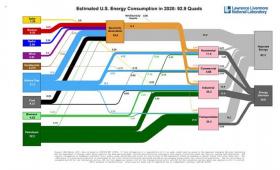
Americans used approximately 7 percent less energy in 2020, due in part to the COVID-19 pandemic, according to energy flow charts released by Livermore.
Science and Technology
in the News
Science and Technology
in the News
News Center

Livermore researchers and their colleagues who help them commercialize technologies have won three national technology transfer awards this year.

A research team uncovered a surprising, self-improving property in a silicon/gallium nitride photosynthesis device that contributes to the material’s highly efficient and stable performance in converting light and water into carbon-free hydrogen.

Researchers are improving the modeling of drizzle in stratocumulus clouds to enhance the accuracy of climate models.

Twenty years of Livermore research has revealed the mechanisms behind plutonium’s slow migration through the environment.

Using a real-world application for quantum mechanics, Laboratory researchers are finding ways to make hydrogen fuel tanks more efficient.

Livermore researchers are developing a simple, yet powerful, health assessment tool for use on the battlefield, in space, or in other isolated settings.

Livermore’s Inertial Confinement Fusion program brings unparalleled value to the nation.
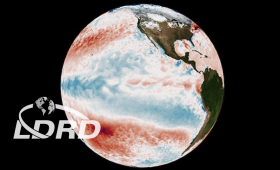
New research shows that naturally occurring climate variations help to explain a long-standing difference between climate models and satellite observations of global warming.
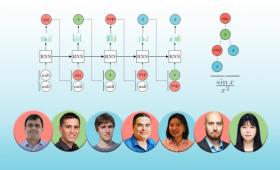
Livermore scientists have developed a new framework and an accompanying visualization tool that leverages deep reinforcement learning for symbolic regression problems,