The DOE announces $134 million in funding for two programs designed to secure U.S. leadership in emerging fusion technologies and innovation.
Science and Technology
in the News
Science and Technology
in the News
News Center

LLNL researchers are tackling this challenge by developing first-of-their-kind approaches to look at how materials and structures evolve inside a metal AM structure during printing.
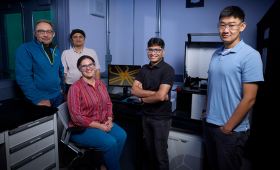
LLNL researchers and collaborators miniaturize quadrupole ion traps for the first time with 3D printing.

MIT Technology Review has named LLNL research scientist Xiaoxing Xia as one of its 2025 Innovators Under 35.
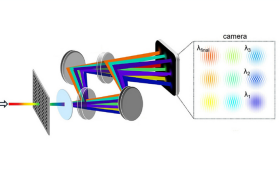
In a study published in Optica, LLNL researchers developed a new diagnostic that captures plasma evolution in time and space with a single laser shot.
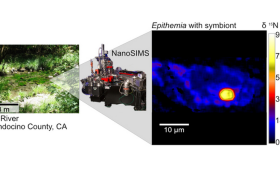
LLNL researchers and collaborators investigated a California river ecosystem and found a nitrogen-fixing bacterium that acts like a proto-organelle.

LLNL physicist Hye-Sook Park wins the Edward Teller Award by the American Nuclear Society.

Diana Chen, an LLNL optical engineer, has been named a Senior Member of SPIE, the international society for optics and photonics.
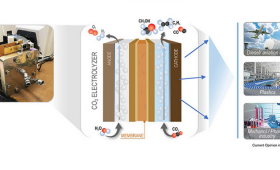
In a new study, LLNL researchers design a new polymer ink, called an ionomer, that controls how gas and water move in electrochemical devices.

The STARFIRE Hub for IFE, led by LLNL, adds five new members to its Diode Technology Working Group.


