Research shows that two-thirds of the increase in vapor pressure deficit, an indication of fire weather, in the western United States is due to human-caused climate change.
Science and Technology Highlights

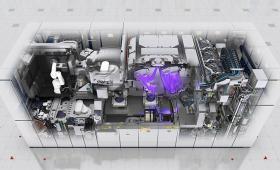
First in a series of articles describing aspects of the National Ignition Facility’s record-breaking 1.3-megajoule experiment.
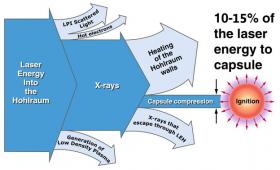
Second in a series of articles describing aspects of the National Ignition Facility’s record-breaking 1.3-megajoule experiment.

A Multi-institutional team of researchers found that late-migrating fish that spend a year in their home streams as juveniles leave in the fall and arrive in the ocean larger and more likely to survive their years at sea.
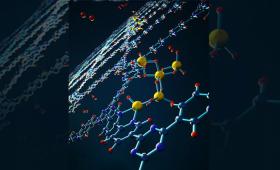
Researchers are exploring the use of metal hydrides to reversibly release and uptake hydrogen under mild conditions.
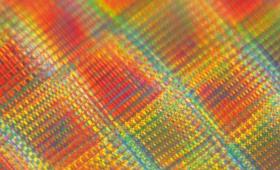
Livermore scientists have created nanostrut-connected tube-in-tubes that enable stronger low-density structural materials.
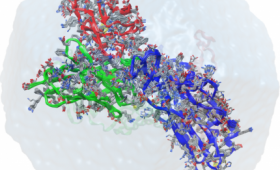
Livermore has joined the international Human Vaccines Project to accelerate vaccine development and understanding of immune response.
The microprocessors at the heart of an increasing number of the world’s newest mobile phones and personal computers were made possible in part by Livermore research.

Livermore has shipped the last of six optical filters for the Vera C. Rubin Observatory telescope’s camera.

Version 2 of the Energy Exascale Earth System Model (E3SM2) is significantly faster than its predecessor and was released to the broader scientific community on September. 28.


