For nearly half a century, the Laboratory has created unique one-page charts that diagram the nation’s energy use and consumption in an easy-to-understand format.
Science and Technology Highlights
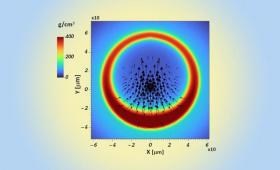
Researchers gain new insights into why small eviations from perfect spherical symmetry can lead to significant distortions of the implosion and ultimately degrade inertial confinement (ICF) fusion performance.

Now in its 11th year, the Lawrence Livermore–Las Positas College Science and Engineering Seminar Series provides Livermore scientists and engineers a forum to share their research with students, faculty, and the Tri-Valley community.

A technology once rejected for fusion power plants now supports a promising new flash neutron imaging capability.
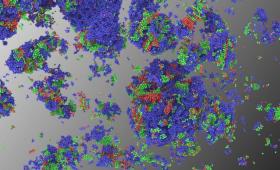
Livermore researchers report on a new mechanism of solidification in copper that alters the fundamental understanding of nucleation at high pressure.

Livermore scientists are leveraging their extensive experience studying the movement of airborne hazards to better understand the movement of virus-like particles through the air.

One year after publishing the groundbreaking "Getting to Neutral: Options for Negative Carbon Emissions in California," Lawrence Livermore has become a trusted adviser in the discussion of how to remove carbon dioxide from the air.
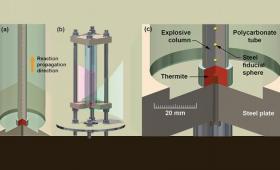
New research is shedding light on the deflagration-to-detonation transition” process to make explosives safer for handling, storage and transportation.
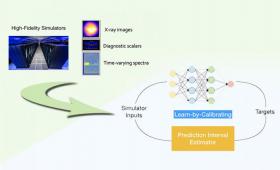
Livermore computer scientists have developed a new deep learning approach to designing emulators for scientific processes that is more accurate and efficient than existing methods.

Researchers have taken important steps to show that thermal conduction is important and measurable at high pressure and temperature conditions.


