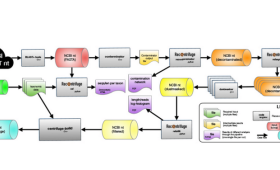
LLNL researchers are working with the National Center for Biotechnology Information's (NCBI) Nucleotide (nt) database to create a vast repository of DNA sequences from across all known species.
Science and Technology Highlights
LLNL researchers, in collaboration with other leading institutions, successfully use an AI-driven platform to preemptively optimize an antibody to neutralize a broad diversity of SARS-CoV-2 variants.
A multi-institutional team of researchers invent 3D-printed, multi-stable structures capable of changing colors in response to stress, with a goal of combining the unique materials and techniques to help redefine smart materials.
Since the 1970s, the Janus laser, now part of JLF, has served as an experimental proving ground to LLNL laser and fusion programs and the broader high-energy-density and laser science communities.
A recent study led by LLNL scientists is offering new insight into modeling complex protein interactions using a combination of detailed molecular simulations and large-scale models.

A research collaboration between LLNL and Pennsylvania State University has generated a portfolio of intellectual property (IP), jointly owned by both organizations, that uses bacterial proteins to pick out critical metal ions.
LLNL and Verne have demonstrate a novel pathway for creating high-density hydrogen.
This episode of the Big Ideas Lab podcast takes a deep dive into how the Innovation and Partnerships Office facilitates tech transfer at LLNL and some of the most impactful success stories over the years.
A recent study from LLNL used a combination of spectroscopy, simulation and machine learning to examine the surface of ice.
New research, published in Nature by a team including LLNL scientists, introduces an experimental technique to constrain the size of the neutrino’s wavepacket.