LLNL researchers are tackling this challenge by developing first-of-their-kind approaches to look at how materials and structures evolve inside a metal AM structure during printing.
Science and Technology Highlights
LLNL researchers and collaborators miniaturize quadrupole ion traps for the first time with 3D printing.
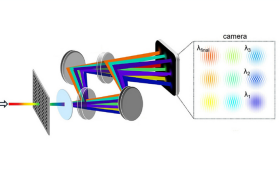
In a study published in Optica, LLNL researchers developed a new diagnostic that captures plasma evolution in time and space with a single laser shot.
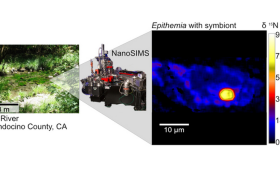
LLNL researchers and collaborators investigated a California river ecosystem and found a nitrogen-fixing bacterium that acts like a proto-organelle.
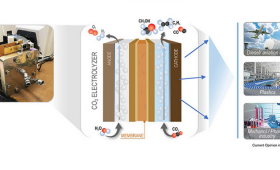
In a new study, LLNL researchers design a new polymer ink, called an ionomer, that controls how gas and water move in electrochemical devices.

The STARFIRE Hub for IFE, led by LLNL, adds five new members to its Diode Technology Working Group.

LLNL researchers create molecular dynamics simulations to explain what material forms when carbon crystallizes.
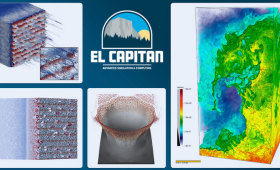
LLNL researchers model extreme physical events with unprecedented resolution, realism and speed.

LLNL researchers analyzed asteroid material to show that its elements reflect the early composition of the solar system.

LLNL researchers employed an AI-driven model to predict fusion ignition days ahead of the historic 2022 shot.


