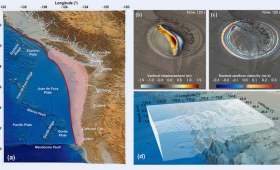
LLNL scientists have helped develop an advanced, real-time tsunami forecasting system that could dramatically improve early warning capabilities.
Science and Technology Highlights
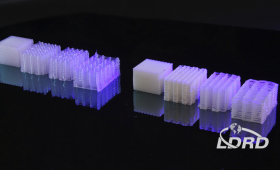
LLNL scientists and collaborators have created a new class of programmable soft materials that can absorb impacts like never before.

Optimax Space Systems have signed a Cooperative Research and Development Agreement (CRADA), expanding production of LLNL’s next-generation space domain awareness technology.

In a new study, LLNL researchers demonstrate a model that can reproduce and explain delta-plutonium’s thermal behavior and unusual properties.

LLNL researchers have reached a milestone in combining AI with fusion target design by deploying AI agents to automate and accelerate inertial confinement fusion (ICF) experiments.

LLNL researchers create a droplet-based platform that uses ions to perform simple neuromorphic computations.
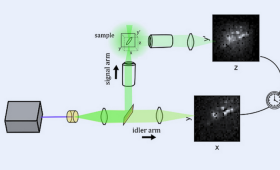
LLNL scientists develop a 3D quantum ghost imaging microscope — the first of its kind.

LLNL is selected to provide a new monolithic telescope for a responsive space mission that will launch as early as 2027.

Under the three-year DeNOVO project, LLNL and other institutions will apply high-performance computing and AI to push the boundaries of antibody design.

In a study published in PNAS Nexus, LLNL researchers described how a new deep learning model is capable of predicting toxic plume behavior in just a few minutes.