LLNL researchers and collaborators are using artificial intelligence and machine learning (AI/ML) to try to find amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) treatments.
Science and Technology Highlights
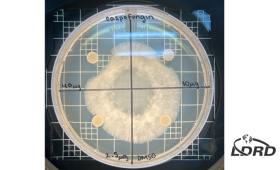
In a study published in the Journal of Microbiological Methods, LLNL researchers combined and refined two established techniques into a new method to screen chemicals for their ability to kill filamentous fungi.
In a new study, published in Analytical Chemistry, LLNL researchers develop a fast and simple approach to screen proteins and their binding properties.

A more than month-long field experiment by an LLNL seismologist demonstrates that a new technology could offer a major breakthrough in seismology.
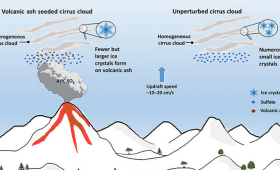
In a study published in Science Advances, LLNL researchers analyzed 10 years of satellite data to determine that volcanic ash particles can trigger cloud formation.
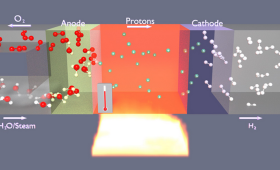
In a new study, published in PRX Energy, LLNL scientists revealed how high operating temperatures could increase electrical leakage in a widely studied fuel cell material.

In a recent study, LLNL researchers presented a new method to deposit quantum-dot films on corrugated surfaces.

LLNL researchers are breaking through the barriers of heavy actinides with a streamlined and efficient “serial approach” for the synthesis and analysis of heavy actinide compounds.

In a new study published in Physical Review Letters, a team of researchers from U.S. universities and national laboratories has set stringent limits on the existence and mass of sterile neutrinos.
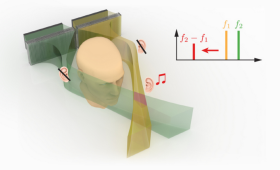
Researchers at Penn State University and LLNL unveil a novel technique that allows sound to be delivered to a precise location, circumventing physical barriers without the need for on-ear devices.

