LLNL and the Extreme Light Infrastructure (ELI) European Research Infrastructure Consortium (ERIC) have signed a new Memorandum of Understanding that builds on their existing strategic collaboration for scientific research and laser innovation.
Science and Technology Highlights

In a recent study, published in Nature, an international team including LLNL researchers experimentally measured the structure of liquid carbon for the first time.

A new cancer drug candidate developed by LLNL and collaborators demonstrates the ability to block tumor growth without triggering a common and debilitating side effect.
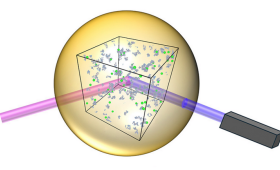
LLNL and collaborators have succeeded in describing warm dense matter much more accurately than before using a new computational method.
In a new study LLNL researchers and collaborators triggered a slow decomposition of a high explosive and measured the effects on the molecules within it.
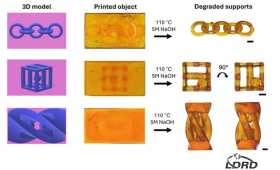
LLNL researchers develop a novel 3D printing technique that uses light to build complex structures, expanding possibilities in multi-material additive manufacturing.

LLNL's state-of-the-art telescope system will be deployed onboard Firefly’s Elytra orbital vehicle to enable Firefly’s new Ocula imaging service.
LLNL flagship exascale machine El Capitan maintained its status as the fastest supercomputer on the planet — claiming the No. 1 spot on three of the most prestigious high-performance computing (HPC) rankings.
LLNL researchers and collaborators are using artificial intelligence and machine learning (AI/ML) to try to find amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) treatments.
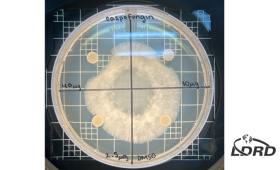
In a study published in the Journal of Microbiological Methods, LLNL researchers combined and refined two established techniques into a new method to screen chemicals for their ability to kill filamentous fungi.

