In November, the Department of Energy Office of Science renewed the Superconducting Quantum Materials and Systems Center.
Science and Technology
in the News
Science and Technology
in the News
News Center

LLNL Director Kim Budil has been elected as a member of the National Academy of Engineering (NAE), one of the highest professional distinctions in the field.

LLNL researchers and collaborators lay the foundation for understanding how POMs interact with some of the most chemically challenging actinide elements.

LLNL researchers aim to use a machine-learning model that can distinguish opioids from other chemicals with an accuracy over 95% in a laboratory setting.

A multidisciplinary team of LLNL researchers has successfully demonstrated a potentially simpler, more accurate way to measure plasma conditions with two laser beams that cross paths.

Staff scientist Elizabeth Grace of LLNL has been awarded the 2026 European Physical Society-Plasma Physics Division (EPS-PPCF) Sylvie Jacquemot Early Career Prize.

In an open-access database and with publicly available code, LLNL researchers have simulated and published one million orbits in cislunar space.
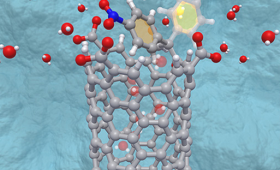
In a recent study, LLNL researchers and collaborators engineered carbon nanotubes with openings that can reversibly open and close depending on pH.
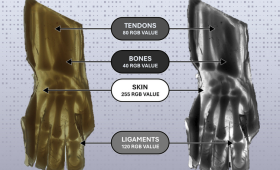
LLNL researchers have co-developed a new way to precisely control the internal structure of common plastics during 3D printing.

Abbas Nikroo, deputy director for physics integration at LLNL's National Ignition Facility, received the 2025 Distinguished Career Award by Fusion Power Associates.


