Lawrence Livermore will lead a National Nuclear Security Administration project with Cornelis Networks to collaborate on next-generation high-performance networking.
Science and Technology Highlights
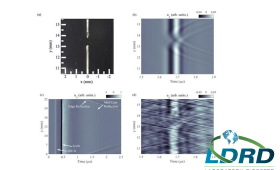
Livermore researchers have developed a new all-optical ultrasound technique capable of performing on-demand characterization of melt tracks and detecting formation of defects in a popular metal 3D printing process.
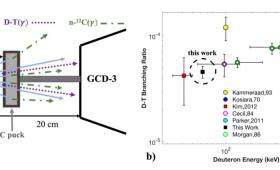
Livermore researchers have refined the measurement of the gamma (γ)-to-neutron branching ratio in deuterium-tritium (D-T) fusion reactions, a result that is relevant to fusion energy.

The Laboratory has signed a memorandum of understanding with the city of Livermore to collaborate on advancing climate action in Livermore

Researchers have demonstrated the ability to 3D-print microscopic objects in silica glass, part of an effort to produce delicate, layer-less optics that can be built in seconds or minutes.

A Livermore climate scientist and collaborators developed a novel approach to more quickly see the temperature response to strong emissions reductions.

LLNL researchers recently learned that they had received an “A” grade for the 12th consecutive year in October’s 50th Organisation for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons proficiency test.

In 2021, Americans used 5% more energy than in 2020, according to the most recent energy flow charts released by the Laboratory.

Livermore’s innovative 3D battery designs increase power density and longevity for remote applications.
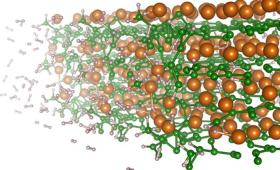
Livermore scientists have simulated the hydrogen storage reactions in a promising material and discovered why hydrogen uptake slows as the material absorbs hydrogen.


