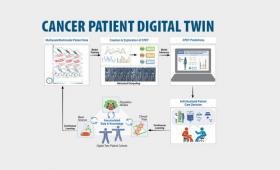
A multi-institutional team has proposed a framework for digital twin models of cancer patients.
Science and Technology Highlights
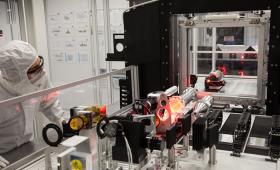
NIF’s lasers delivered slightly more than the requested 1.9 megajoules (MJ) of laser energy at 440 terawatts of peak power for the shot that produced a historic 1.35 megajoules of fusion energy.
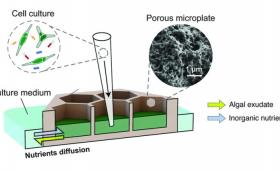
A multi-institutional research team created a new co-culture device, dubbed a “porous microplate,” to study how metabolites in the water affect the growth of bacterial communities.

Among the factors contributing to the National Ignition Facility (NIF)’s record-smashing 1.3-megajoule (MJ) energy-yield shot on Aug. 8 was the quality of the high-density carbon (HDC), or diamond, target capsule used in the experiment.

Researchers have shown for the first time the potential for linear induction accelerators (LIAs) to deliver effective, targeted doses of “FLASH” radiation to cancer patients.

The Laboratory is taking part in NASA’s first-ever planetary defense test, which deliberately collides a spacecraft into an asteroid called Dimorphos.

Rock weathering — the process of chemical transformation by long exposure to water and the atmosphere — boosts soil organic carbon storage by altering soil mineralogy.

A research team has dveloped a machine learning-based technique capable of automatically deriving a mathematical model for the motion of binary black holes from raw gravitational wave data.

Third in a series of articles describing aspects of the National Ignition Facility’s record-breaking 1.3-megajoule experiment.

Research shows that two-thirds of the increase in vapor pressure deficit, an indication of fire weather, in the western United States is due to human-caused climate change.