Laboratory recipients of the Department of Energy’s Office of Science Early Career Research Program awards continue to make advances in fundamental science research.
Science and Technology Highlights

Livermore scientists and their collaborators have developed an open-source, high-performance simulator for studying large-scale geological carbon dioxide storage.

A White House summit convened leaders in fusion from government, industry, and academia, including Laboratory Director Kim Budil, to discuss a strategy for developing commercial fusion energy.

The Laboratory’s cybersecurity, data science, and systems-engineering expertise provides layered, strategic protection for electrical grids, water utilities, railways, and pipelines
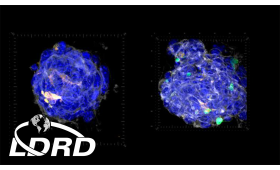
Livermore scientists found that proteins in the extracellular matrix (ECM) can dramatically impact the immune system’s ability to kill tumors.

Livermore researchers and their colleagues are exploring ways to build laser optics from plasma.

Livermore’s decades of leadership in developing high-energy lasers is being tapped to provide a key component of a major upgrade to SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory’s Linac Coherent Light Source.

A new study by researchers at Lawrence Livermore and the University of California, San Francisco, identifies cancer-related risks for poor outcomes from COVID-19.
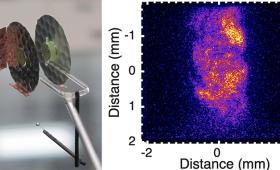
An international team turned to Lawrence Livermore’s National Ignition Facility to help unravel the inner workings of heat conduction in clusters of galaxies—the largest structures in the universe.

In findings that could help advance another “viable pathway” to fusion energy, research led by Livermore physicists has proven the existence of neutrons produced through thermonuclear reactions from a sheared-flow stabilized Z-pinch device.