A prototype, field-deployable device offers postdetonation debris analysis following a nuclear event.
Science and Technology Highlights

A high-explosive experiment at the National Ignition Facility expands understanding of material characteristics.

New approaches to artificial intelligence improve machine-learning predictions in real-world applications.

A Livermore report outlines a strategy to reduce California’s carbon emissions to net zero by 2045.
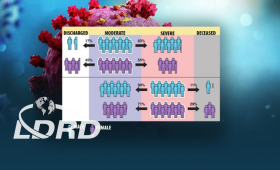
A Livermore team has developed a comprehensive dynamic model of COVID-19 disease progression in hospitalized patients, finding that risk factors for complications from the disease are dependent on the patient’s disease state.

Two of the fields that stand to gain from the National Ignition Facility’s record shot are stockpile stewardship science and the quest for inertial fusion energy (IFE).

Livermore, Penn State, and University of Arizona researchers are partnering with industry collaborator Western Rare Earths, U.S. subsidiary of American Rare Earths Limited, to use a naturally occurring protein to extract and purify rare earth elements from abundant, domestic ore-based feedstocks and waste materials without harming the environment.

Increasingly sophisticated computational models and simulations helped guide the National Ignition Facility’s record-breaking 1.3-megajoule experiment.

Livermore and ELI-Beamlines in the Czech Republic have reached a major agreement to ramp up performance of the L3-High-Repetition-Rate Advanced Petawatt Laser System to its full design capabilities.
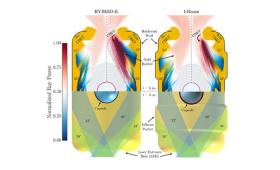
The target and laser designs that achieved a burning plasma state on November 2020 and February 2021 at the National Ignition Facility are described in a Nature paper.


