Livermore has deployed “Ruby,” a high performance computing cluster that will perform functions for the National Nuclear Security Administration and support the Laboratory’s COVID-19 research.
Science and Technology Highlights
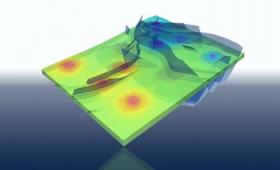
Livermore, Total, and Stanford University are releasing an open-source, high-performance simulator for large-scale geological carbon dioxide storage.

Livermore and its partners AMD, Supermicro and Cornelis Networks have installed a new high-performance computing (HPC) cluster with memory and data storage capabilities optimized for data-intensive COVID-19 research and pandemic response.

Livermore scientists and collaborators have created a new conceptual framework as well as a simulation model that traces the path of individual carbon atoms as they interact with the environment.

Livermore researchers have adapted a new class of materials for their groundbreaking volumetric 3D printing method, greatly expanding the range of material properties achievable.

A research team has identified paleowater—water that recharged before the Holocene started 12,000 years ago—using three key isotopic indicators of groundwater residence time
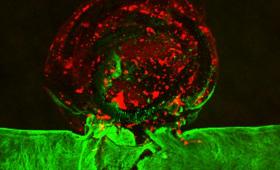
Medical practitioners may be able to improve existing treatment methods and develop new personalized ones for brain aneuryms, thanks to researchers at Livermore and their outside collaborators.

LLNL has installed a state-of-the-art artificial intelligence accelerator from SambaNova Systems, allowing researchers to more effectively combine AI and machine learning with complex scientific workloads.

An LLNL team solved a mystery of metallurgy by simulating the metal hardening process.
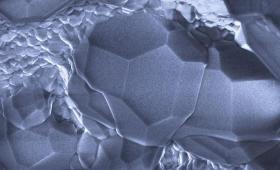
A multi-institutional research team synthesized methane hydrate with sediments to determine the electrical conductivity of the mixtures.


