An LLNL team solved a mystery of metallurgy by simulating the metal hardening process.
Science and Technology Highlights
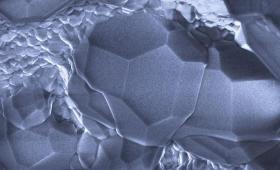
A multi-institutional research team synthesized methane hydrate with sediments to determine the electrical conductivity of the mixtures.

Livermore researchers have created carbon nanotube pores that are so efficient at removing salt from water they are comparable to commercial desalination membranes.
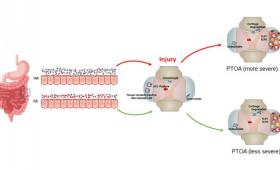
Researchers find that pre-treating joints with antibiotics reduces inflammation from post-traumatic osteoarthritis following a traumatic joint injury.
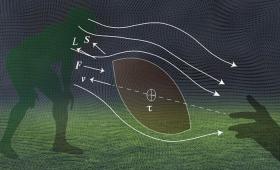
A team of researchers resolves the paradox of the tight spiraling of the tip of a perfectly thrown football around the trajectory of its parabolic path of flight.
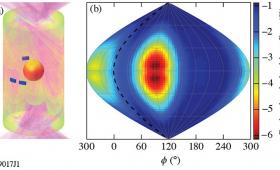
Data correlating two factors that lead to implosion asymmetries have brought LLNL scientists a step closer to understanding the gap between simulations and performance of inertial confinement fusion experiments.
Livermore scientists have paired 3D-printed, living human brain vasculature with advanced computational flow simulations to better understand tumor cell attachment to blood vessels.

Researchers find that more than 50 percent of the world’s oceans already could be impacted by climate change.
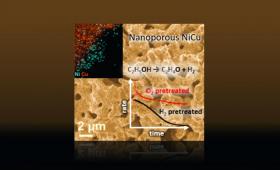
A research team optimizes catalyst performance by studying the effect of pretreatment-induced nanoscale structural and compositional changes on catalyst activity and long-term stability.



